Graduate research demands more than deep thinking—it requires managing an increasingly complex workflow of finding sources, organizing knowledge, writing drafts, and collaborating with advisors. The right tools can save hundreds of hours over a degree program while improving the quality of your work. This guide covers essential tools across seven categories, helping you build a research toolkit tailored to your discipline, budget, and working style.
5 Şub 2026
By

Joe Pacal, MSc
TL;DR
Every graduate researcher needs tools in four core areas: reference management (Zotero is the go-to free option), literature discovery (combine Google Scholar with an AI tool like Semantic Scholar or Wonders), writing support (Grammarly or Writefull for editing, Overleaf or Google Docs for drafting), and knowledge management (Notion or Obsidian for notes). Start with free tools, then add paid options only when you hit clear limitations. Your toolkit will evolve—what works in coursework may not suit dissertation writing.
Reference Management
Reference managers are the backbone of academic research. They store your sources, generate citations, and build bibliographies automatically. If you only adopt one tool from this guide, make it a reference manager.
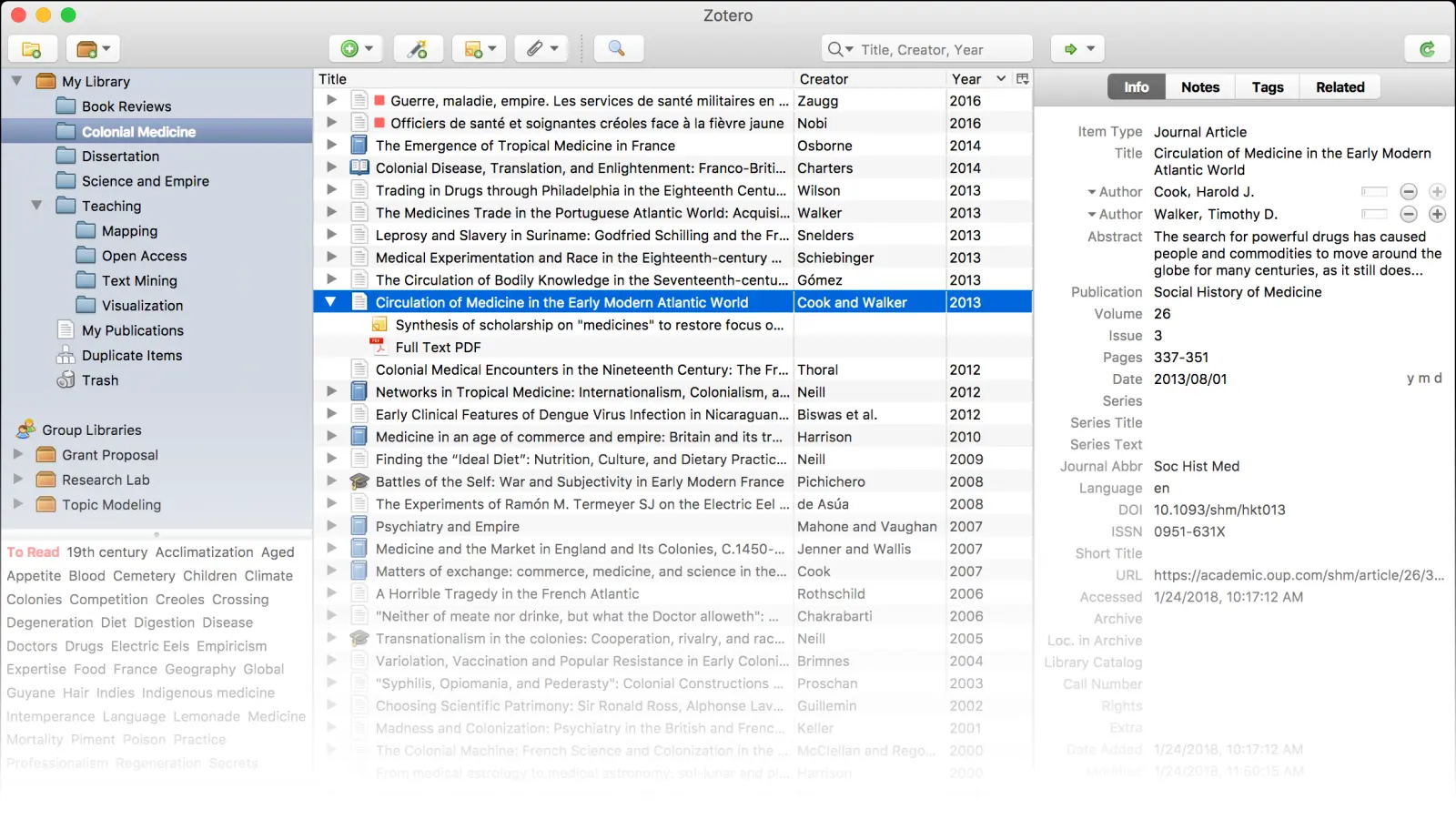
Zotero
Zotero is a free, open-source reference manager that has become the standard recommendation for graduate students. Its browser extension captures sources with one click, automatically retrieving metadata from databases, library catalogs, and websites.
Why researchers love it:
Completely free with generous storage
Works with any citation style (thousands available)
Group libraries for lab collaboration
PDF storage and annotation
Plugin ecosystem (Zotfile, Better BibTeX)
Strong privacy—you control your data
Limitations: Interface feels dated compared to newer tools; mobile apps are basic.
Pricing: Free (300MB sync) | Storage from $20/year (2GB)
Mendeley
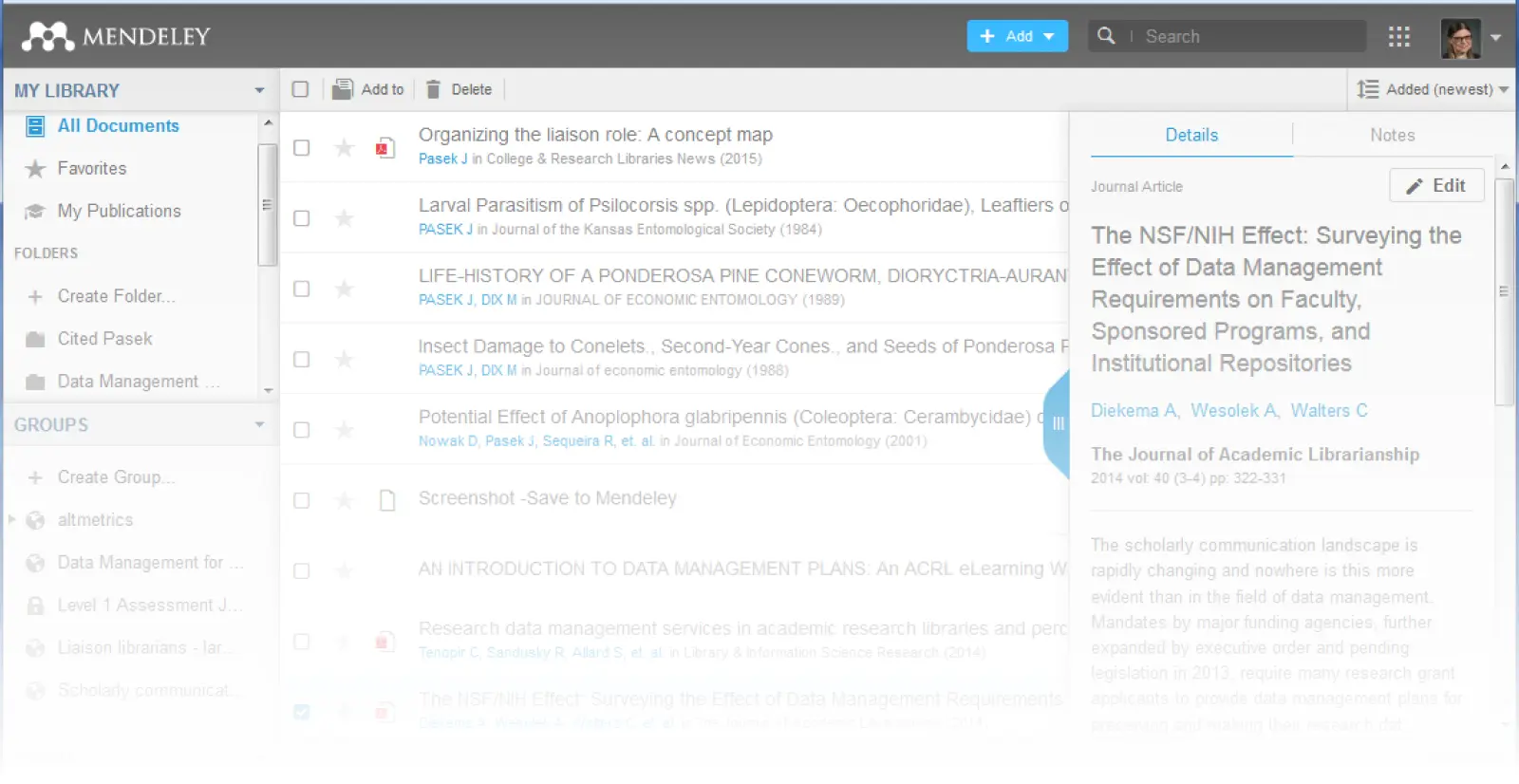
Mendeley combines reference management with PDF reading and an academic social network. Owned by Elsevier, it integrates smoothly with Scopus and ScienceDirect databases.
Why researchers love it:
Built-in PDF reader with annotation
Paper recommendations based on your library
Strong institutional adoption means easy collaboration
Automatic metadata extraction from PDFs
Limitations: Elsevier ownership concerns some researchers; recent interface changes frustrated long-time users.
Pricing: Free (2GB) | Institutional access common
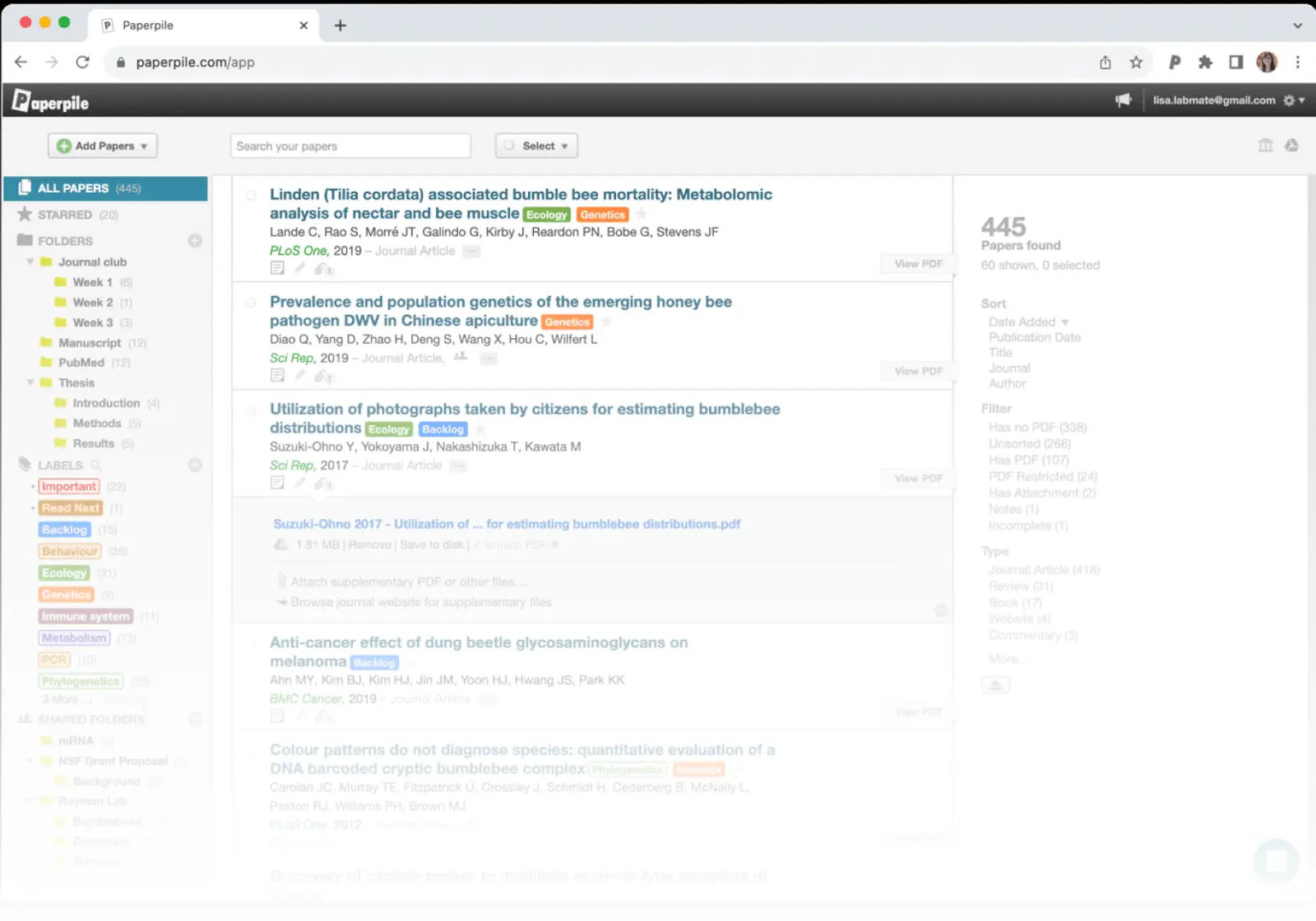
Paperpile
Paperpile is a modern, cloud-native option built for Google Workspace users. Its Google Docs integration is seamless, making it ideal for researchers who write collaboratively.
Why researchers love it:
Fastest, cleanest interface in the category
Native Google Docs citation plugin
Excellent mobile apps
Simple sharing and collaboration
Limitations: No free tier; requires paid subscription.
Pricing: $2.99/month (academic) | $9.99/month (regular)
Reference Manager Comparison
Tool | Free Tier | Best For | Platform | Collaboration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Yes | Budget-conscious, privacy-focused | Desktop + Web | Group libraries | |
Yes | Elsevier users, PDF reading | Desktop + Web | Groups + social | |
No | Google Workspace users | Web + Mobile | Shared folders | |
No | Institutional users, complex needs | Desktop | Shared libraries |
Literature Discovery & Search
Finding relevant papers efficiently separates productive researchers from those drowning in irrelevant results. Modern AI tools have transformed discovery beyond simple keyword matching.
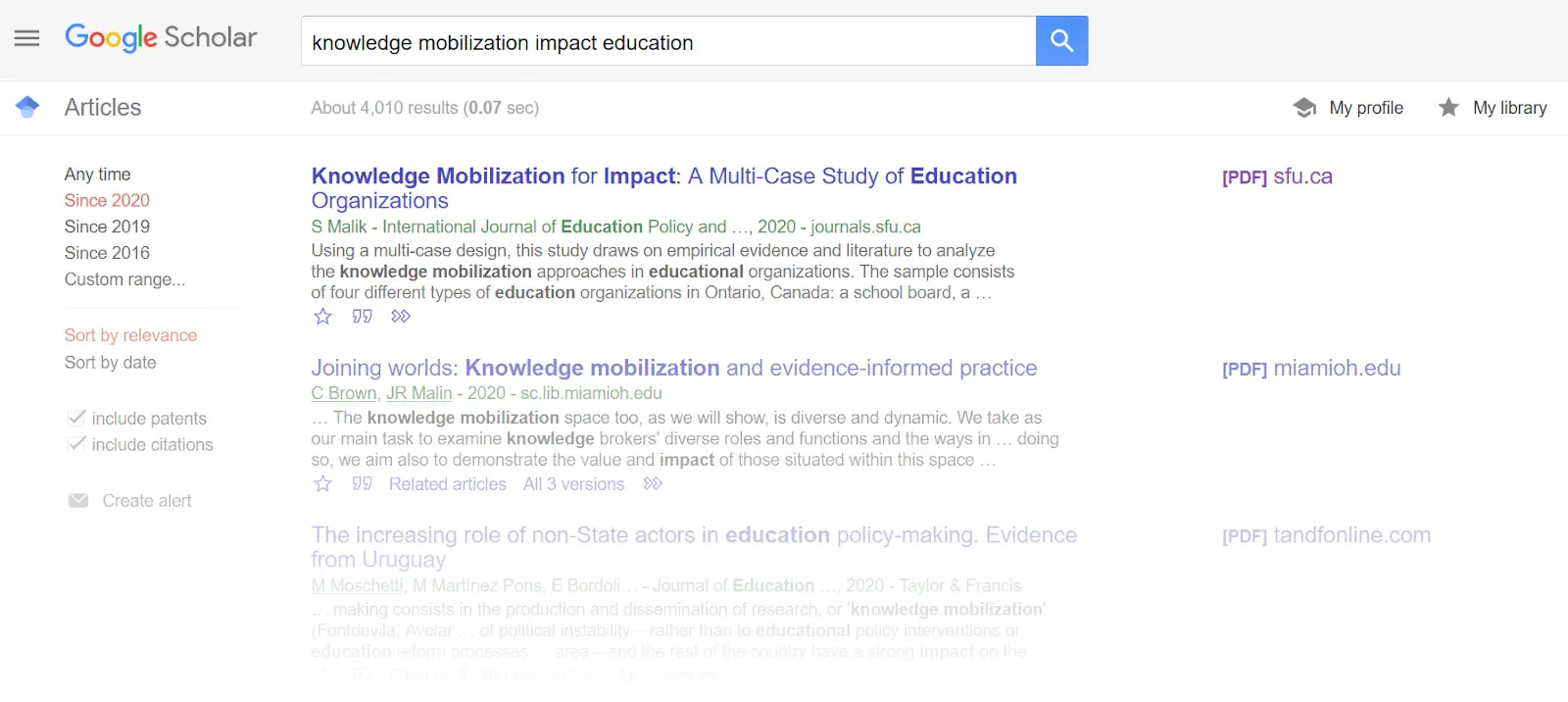
Google Scholar
Google Scholar remains the starting point for most searches due to its comprehensive coverage and familiar interface. It indexes papers, theses, books, and preprints across publishers and repositories.
Why researchers love it:
Broadest coverage of any academic search
Free, no account required
"Cited by" and "Related articles" features
Alerts for new papers on topics
Library links for full-text access
Limitations: No quality filtering; search algorithms are opaque; metadata can be messy.
Pricing: Free
Semantic Scholar
Semantic Scholar applies AI to academic search, offering features like paper summaries (TLDRs), citation context, and influence scores. It's particularly strong for computer science, biomedicine, and related fields.
Why researchers love it:
AI-generated paper summaries
Shows how citations are used in context
Research feeds track your interests
Semantic Reader for enhanced PDF experience
Limitations: Coverage gaps outside core fields; some features require account.
Pricing: Free
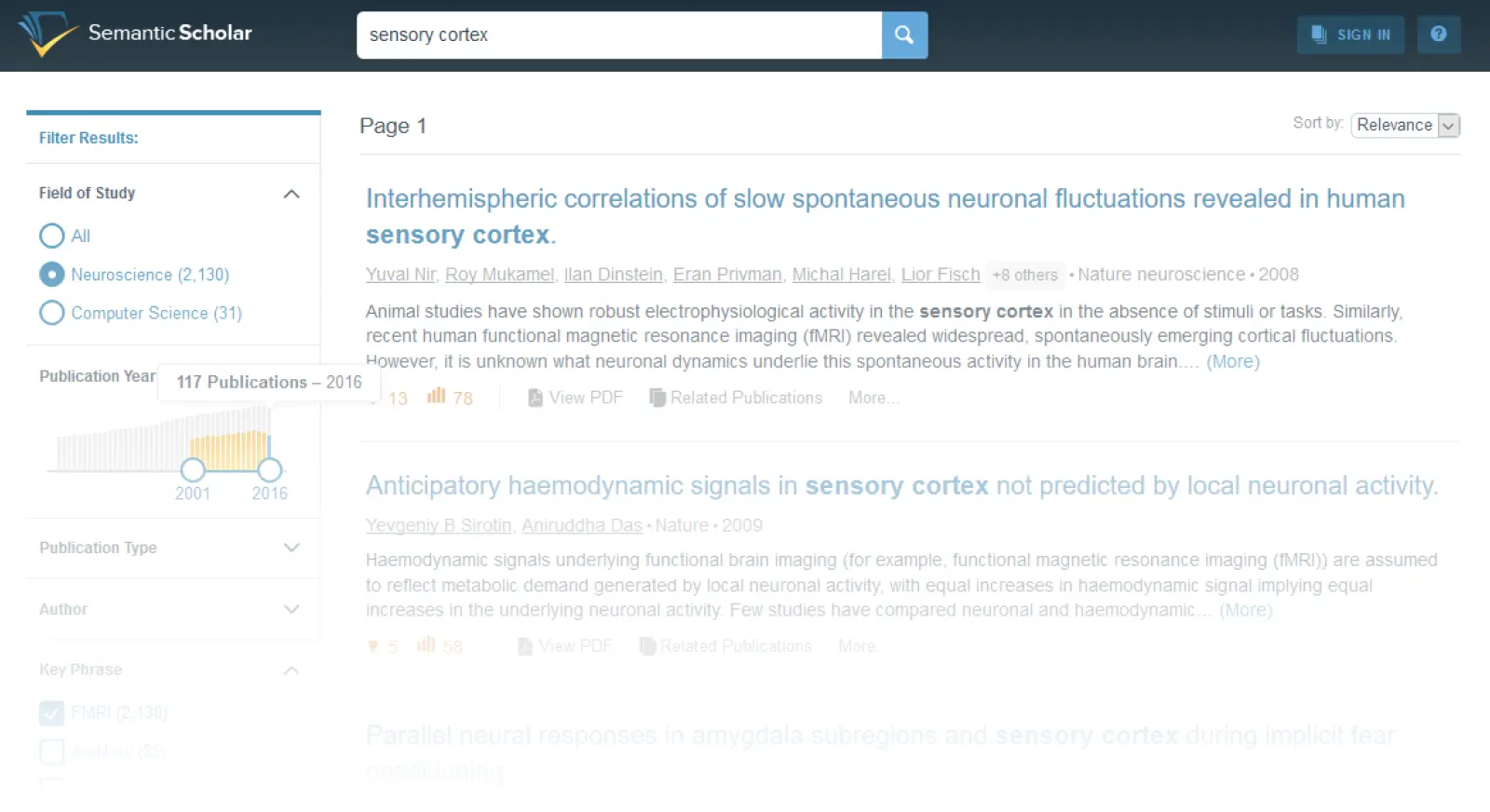
Connected Papers
Connected Papers visualizes relationships between papers, helping you discover the intellectual landscape around a topic. Start with one paper and see what it builds on and what builds on it.
Why researchers love it:
Visual citation graphs reveal hidden connections
Great for finding foundational papers
Easy export to reference managers
Works with any seed paper
Limitations: Limited to citation relationships; monthly limit on free tier.
Pricing: Free (5 graphs/month) | Pro $6/month
Wonders
Wonders is an AI research workspace that combines many features of the tools above—from literature discovery with organization and writing support. Unlike tools designed only for experienced researchers, Wonders focuses on guiding students through the research process—teaching skills while helping complete tasks.
Why researchers love it:
Guided search helps develop research skills
Transparent AI process shows reasoning
Organization tools keep projects manageable
Writing assistance with proper citations
Particularly valuable for students and ESL researchers
Limitations: Newer platform with growing features.
Pricing: Free 21-day trial | Pro plans at readwonders.com/pricing
Discovery Tools Comparison
Tool | AI Features | Coverage | Best For | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Basic | Broadest | Starting searches | Free | |
Strong | CS, Bio, Med | Quick paper assessment | Free | |
Partial | Citation-based | Visual exploration | Freemium | |
Strong | Growing | Guided research | Freemium | |
Strong | Broad | Systematic extraction | Freemium |
Writing & Grammar Tools
Academic writing has distinct conventions that general writing tools don't always understand. These tools help you write clearer, more precise prose appropriate for scholarly audiences.
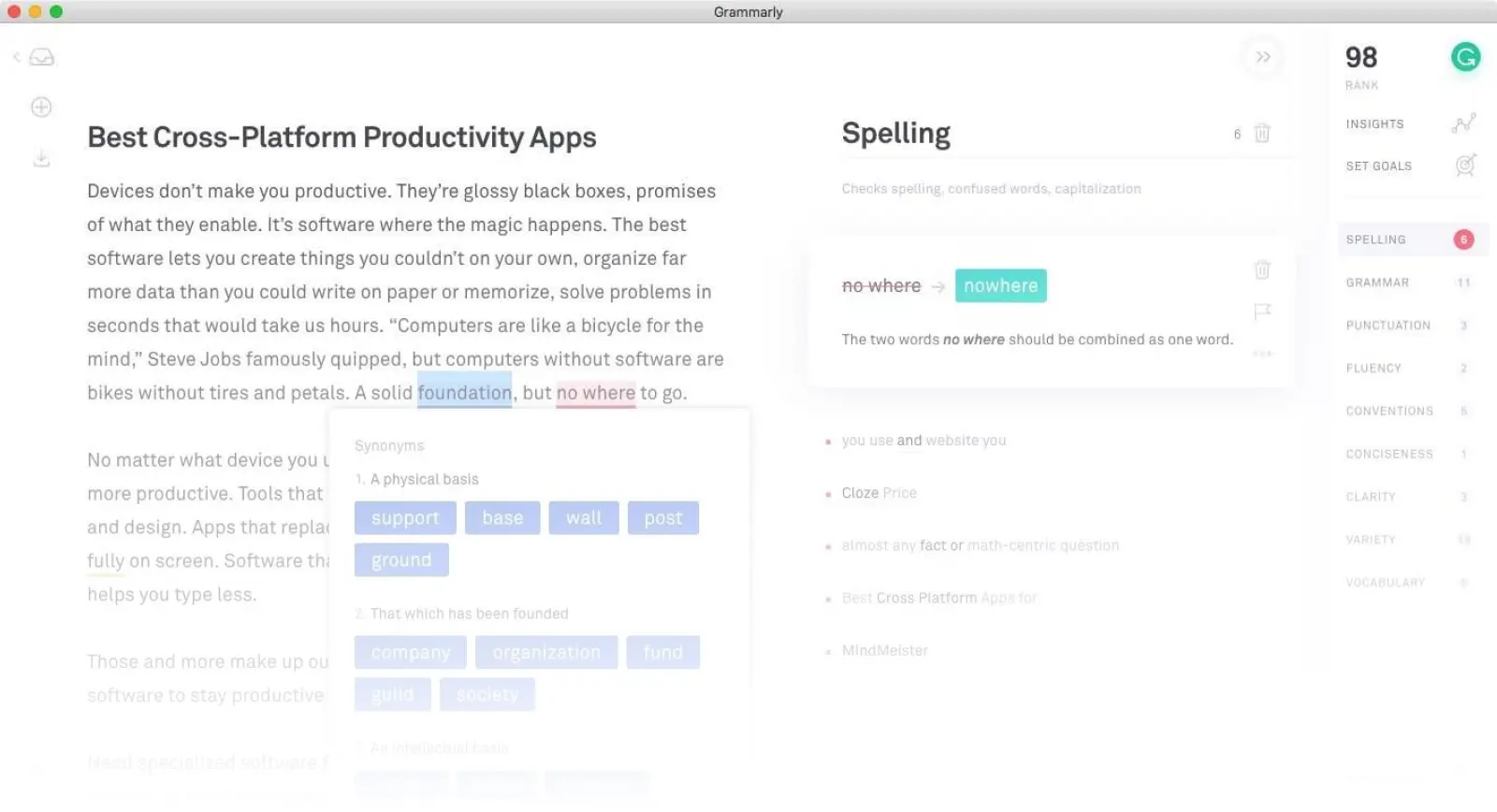
Grammarly
Grammarly is the most widely-used writing assistant, catching grammar errors, suggesting clarity improvements, and checking for plagiarism. While not academic-specific, its broad utility makes it valuable for emails, drafts, and polished manuscripts alike.
Why researchers love it:
Works everywhere (browser, Word, desktop)
Catches errors other tools miss
Tone and clarity suggestions
Plagiarism checking (Premium)
Limitations: Some suggestions don't fit academic register; premium is pricey.
Pricing: Free (basic) | Premium $12/month (annual) | Student discounts available
Writefull
Writefull is specifically designed for academic writing, trained on millions of published papers. It understands disciplinary conventions and offers suggestions appropriate for scholarly prose.
Why researchers love it:
Academic-specific language models
Sentence palette with published examples
Paraphrasing tool for rewording
Integrates with Overleaf
Limitations: Narrower scope than Grammarly; less useful for non-academic writing.
Pricing: Free (limited) | Premium €9.95/month
ProWritingAid
ProWritingAid offers deeper stylistic analysis than most tools, with reports on readability, sentence variety, and overused words. Many writers use it for substantive revision rather than just proofreading.
Why researchers love it:
Detailed style reports
Consistency checking
Works in many apps including Scrivener
One-time purchase option available
Limitations: Learning curve; can be overwhelming for quick edits.
Pricing: Free (limited) | Premium $10/month | Lifetime $399
Writing Tools Comparison
Tool | Academic Focus | Best Feature | Platform | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
General | Ubiquity | Everywhere | Freemium | |
High | Academic models | Word, Overleaf | Freemium | |
Medium | Style reports | Desktop, Web | Freemium |
Writing & Collaboration Platforms
Beyond checking grammar, you need a place to actually write. These platforms handle drafting, version control, and collaboration with co-authors and advisors.
Overleaf
Overleaf is a collaborative LaTeX editor used widely in STEM fields. It handles compilation in the cloud, eliminating setup headaches, and enables real-time collaboration on complex documents.
Why researchers love it:
No LaTeX installation needed
Real-time collaboration
Huge template library
Git integration for version control
Direct submission to many journals
Limitations: LaTeX learning curve; paid plans needed for features like track changes.
Pricing: Free (basic) | Student $8/month | Standard $15/month
Google Docs
Google Docs remains a solid choice for collaborative writing, especially in humanities and social sciences where LaTeX isn't standard. Its commenting and suggestion features make it excellent for advisor feedback.
Why researchers love it:
Real-time collaboration that just works
Comments and suggestions for feedback
Version history
Works in any browser
Integrates with Paperpile and Zotero
Limitations: Less control than Word; formatting can be finicky for long documents.
Pricing: Free
Scrivener
Scrivener is a writing application designed for long-form projects like dissertations and books. Its organizational features—corkboard, outliner, split-screen—help manage complex documents.
Why researchers love it:
Built for book-length projects
Flexible organization (chapters, sections, notes)
Research folder for source materials
Compile to multiple output formats
Distraction-free writing mode
Limitations: Desktop only; learning curve; no real-time collaboration.
Pricing: $49 (one-time) | Educational discount available
Writing Platform Comparison
Tool | Best For | Collaboration | Learning Curve | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
STEM, math-heavy | Real-time | High (LaTeX) | Freemium | |
General, humanities | Real-time | Low | Free | |
Universal acceptance | Track changes | Low | Paid/Institutional | |
Long documents | None | Medium | One-time |
Knowledge Management & Note-Taking
Research generates mountains of notes, ideas, and connections. Knowledge management tools help you capture, organize, and retrieve insights when you need them.
Notion
Notion is an all-in-one workspace combining notes, databases, wikis, and project management. Many researchers use it to organize everything from reading notes to dissertation outlines.
Why researchers love it:
Extremely flexible—build what you need
Database views for literature tracking
Templates for common workflows
Works across devices
Free for personal use
Limitations: Can become overwhelming; offline access limited.
Pricing: Free (personal) | Plus $8/month
Obsidian
Obsidian is a Markdown-based note-taking app that emphasizes linking ideas together. Its graph view visualizes connections between notes, supporting the kind of non-linear thinking research requires.
Why researchers love it:
Backlinks connect related ideas automatically
Local files—you own your data
Graph view shows knowledge structure
Massive plugin ecosystem
Works offline
Limitations: Less polished than Notion; requires comfort with plain text.
Pricing: Free (personal) | Sync $4/month | Publish $8/month
Logseq
Logseq combines outlining, note-taking, and task management in a daily-journal format. Its bidirectional linking and query features make it popular for building personal knowledge bases.
Why researchers love it:
Open source and privacy-focused
Block-level references
PDF annotation built-in
Local-first with optional sync
Limitations: Different paradigm requires adjustment; less visual than Notion.
Pricing: Free | Sync in beta
Knowledge Management Comparison
Tool | Approach | Best For | Data Storage | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Databases + docs | Visual organizers | Cloud | Free/Paid | |
Linked Markdown | Power users | Local | Free/Paid | |
Outliner + links | Journal-style thinkers | Local | Free | |
Networked thought | Heavy linkers | Cloud | $15/month |
Data Analysis & Visualization
Many research projects require analyzing data and creating figures. These tools range from code-based environments to point-and-click applications.
R + RStudio
R is a programming language for statistical computing, and RStudio is the most popular environment for writing R code. Together, they're the standard for statistics in many social and biological sciences.
Why researchers love it:
Powerful statistics packages
Publication-quality graphics (ggplot2)
R Markdown for reproducible reports
Large community and resources
Free and open source
Limitations: Steep learning curve; programming required.
Pricing: Free
Python + Jupyter
Python with Jupyter Notebooks is increasingly popular for data science, machine learning, and computational research. Notebooks combine code, output, and narrative in a single document.
Why researchers love it:
Versatile beyond statistics
Strong machine learning libraries
Jupyter notebooks are shareable and reproducible
Growing dominance in many fields
Free and open source
Limitations: Learning curve; environment management can be tricky.
Pricing: Free
Tableau / SPSS / Stata
Commercial tools like Tableau (visualization), SPSS (statistics), and Stata (econometrics) remain important in specific disciplines. Check what your department supports before investing time.
Pricing: Varies; often available through institutional licenses
Data Tools Comparison
Tool | Type | Best For | Learning Curve | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Programming | Statistics, graphics | High | Free | |
Programming | ML, computation | High | Free | |
Point-and-click | Traditional stats | Medium | Paid | |
Visualization | Dashboards, exploration | Medium | Freemium |
Productivity & Project Management
Research projects—especially dissertations—span months or years. These tools help you stay organized, meet deadlines, and maintain momentum.
Trello / Asana / Todoist
Task management apps help break large projects into actionable steps. Trello uses visual boards, Asana handles complex project structures, and Todoist offers streamlined task lists.
When to use them: Dissertation milestones, literature review phases, manuscript revision checklists.
Pricing: All have free tiers sufficient for individual researchers.
Calendly / When2meet
Scheduling tools like Calendly eliminate email back-and-forth when booking advisor meetings, committee appointments, or research interviews.
Pricing: Free tiers available
Focus Tools
Apps like Forest, Freedom, and the Pomodoro Technique help maintain focus during deep work sessions—essential for reading dense papers or writing challenging sections.
Building Your Toolkit: Recommendations by Stage
Coursework & Early Research
Start with free tools that establish good habits:
Reference manager: Zotero
Discovery: Google Scholar + Semantic Scholar
Notes: Notion or Obsidian
Writing: Google Docs + Grammarly (free)
Estimated cost: $0
Thesis/Dissertation Phase
Add specialized tools as needs clarify:
Reference manager: Zotero or Paperpile
Discovery: Google Scholar + Wonders or Elicit
Organization: Notion + Zotero collections
Writing: Scrivener or Overleaf + Writefull
Analysis: R/Python as needed
Estimated cost: $10-30/month
Prolific Publishing
Optimize for efficiency and polish:
Reference manager: Paperpile (for speed)
Discovery: Full toolkit based on field
Writing: Overleaf + Writefull + Grammarly Premium
Collaboration: GitHub for code, Overleaf for manuscripts
Estimated cost: $30-50/month


